 Nannochloropsis’ whole cells were recently analysed using 13C-SS-NMR spectroscopy (reference n 1). Cells were grown autotrophically in a sodium [13C] bicarbonate environment and harvested during the exponential phase.
Nannochloropsis’ whole cells were recently analysed using 13C-SS-NMR spectroscopy (reference n 1). Cells were grown autotrophically in a sodium [13C] bicarbonate environment and harvested during the exponential phase.
Quantitative spectra of 13C labelled cells of Nannochloropsis oculata were analysed for resonance picks which are characteristic of carbohydrates and lipids, thus providing, among other interesting observations, useful insights on the cell wall composition of the microalga.
Carbohydrate resonances in microalgae are expected from the cell walls, the headgroup of galactolipids and the storage polysaccharides.
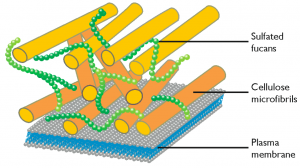
Cell wall
Analysis of the RINEPT and CP spectra of N. oculata allowed to detect resonances in which chemical shifts agreed with those reported for cellulose. The cellulose anomeric carbon C1 only appeared in the rigid (CP) spectrum, the remaining carbons showed up in the spectra of both rigid and mobile zones. The cellulose was attributed to the cell wall (reference n 1). Analysis of the genes present in Nannochloropsis genome also showed the presence of a full set of genes that can be attributed to pathways leading to synthesis and modification of cellulose (reference n 2).
Storage sugars
Chemical shifts corresponding to both β-(1 → 3) and β-(1 → 6) glycans were detected and assigned to chrysolaminarin. Also in this case some of the resonances were exclusively detected in the CP spectra but the remaining resonances appeared on both rigid and mobile zones. The relative mobility observed could be compatible with the accumulation of chrysolaminarins in solution inside the vacuoles (reference n 1). In this case again genes associated to the biosynthesis of chrysolaminarins are found in the genome (reference n 2).
Lipids
Quantitative and qualitative analysis of the lipid content of various Nannochloropsis cultures based on MASS-spectrometry were previously reported (references n 3 and n 4). In this recent work by Arnold and coworkers (reference n 1) lipid signals were analysed from 13C-SS-NMR spectra of whole cells grown photoautotrophically.
The peak assignment showed the presence of galactosyldiacylglycerols. Peaks characteristic of the sulfolipid sulfoquinovosyl-diacylglycerol (SQDG) sugar head group seemed present on both the rigid (CP) and dynamic (RINEPT) spectra. The sugar moieties were better evidenced on the RINEPT spectrum while the glycerol moieties appeared better in the CP spectrum. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) was the dominant phospholipid detected and assigned to the plasma membrane.
The CP and RINEPT spectra were dominated by lipids’ methylene signal (30–33 ppm) consistent with a high content in saturated and mono-unsaturated fatty acid chains. The RINEPT spectrum also showed a strong signal at 128–130 ppm consistent with a high proportion of PUFAs, and possibly to EPA from the vacuolar and mobile TAGs.
For further reading on the subject I suggest of course to read the paper
References
- Arnold AA, Genard B, Zito F, Tremblay R, Warschawski DE, Marcotte I. “Identification of lipid and saccharide constituents of whole microalgal cells by 13C solid-state NMR.” Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Biomembranes. (2014) doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.07.017
- Corteggiani Carpinelli E, Telatin A, Vitulo N, Forcato C, D’Angelo M, Schiavon R, Vezzi A, Giacometti GM, Morosinotto T, Valle G. “Chromosome scale genome assembly and transcriptome profiling of Nannochloropsis gaditana in nitrogen depletion.” Molecular Plant (2014) 7 (2): 323-335. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst120.
- Li J, Han D, Wang D, Ning K, Jia J, Wei L, Jing X, Huang S, Chen J, Li Y, Hu Q, Xu J “Choreography of Transcriptomes and Lipidomes of Nannochloropsis Reveals the Mechanisms of Oil Synthesis in Microalgae.” The Plant Cell April 2014. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.121418
- Simionato D, Block MA, La Rocca N, Jouhet J, Maréchal E, Finazzi G, Morosinotto T. (2013) The response of Nannochloropsis gaditana to nitrogen starvation includes de novo biosynthesis of triacylglycerols, a decrease of chloroplast galactolipids, and reorganisation of the photosynthetic apparatus. Eukaryotic Cell May 2013 vol. 12 no. 5 665-676

A collection of microalgae cultures at CSIRO Marine Research. Image released by CSIRO under Creative Commons Attribution license http://scienceimage.csiro.au/tag/algae/i/1938/microalgae-collection/
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) has just released its Scientific Image Library under a Creative Commons Licence.
Among the many available pictures and images a small section is also dedicated to the microalgal collection of the institute. Following this link you can browse and freely download useful high quality images for lectures, reports and blog posts.
Do not forget that various collection of high quality images released under Creative Common licence already exist and some of them contain images and pictures of microalgae. For instance The Wikimedia Commons Scientific Images Collection. Don’t forget that you can easily upload your pictures and images of Nannochloropsis to the wikimedia commons collection too, as I did some time ago: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:NannochloropsisMinusNitrogenNileRed.jpg
]]>
After manual review by the NCBI experts, the genomic data of Nannochloropsis gaditana B-31 are now indexed in the NCBI databases and are accessible through the NCBI web interface and through the NCBI search tools (e.g. blast).

The genomes of the nucleus and of the organelles and the complete annotation of the genomic sequences are registered as bioproject PRJNA170989 ID: 170989, and can be accessed through the following links:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/170989 ;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/585113370
The sequencing data used to assembly of the genomes were also submitted to the NCBI SRA database and are available for consulting and download. You can find the data of: a fragment library of Nannochloropsis gaditana B-31 whole genomic DNA (i.e. includes DNA from the nucleus and from the organelles) sequenced using 454FLX Titanium XL sequencing kit, 2 half plates (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/SRX390591); a mate pair library of Nannochloropsis gaditana B-31 whole genomic DNA with an insert size of 1.5-3Kb sequenced using the SOLiD 3 Plus sequencing kit, half plate (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/SRX390674); a mate pair library of Nannochloropsis gaditana B-31 whole genomic DNA with an insert size of 3-5Kb sequenced using the SOLiD 3 Plus sequencing kit, half plate (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/SRX390681). Note that details about the biosamples and about the experiments are linked o the data.
The transcriptomic data obtained after cultivation of N. gaditana B-31 in nitrogen sufficient and nitrogen depleted media are collected in bioproject PRJNA174770 ID: 174770, and you can consult and download them at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/174770. Note that the bioproject contains also entries that report details about the biosamples used in the experiments and details about the experiments.
An umbrella project that contains the links to all the bioprojects related to N. gaditana B-31 and submitted to the NCBI to date, has the following accession numbers: PRJNA231651 ID: 231651 and url: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/231651
The publication that describes the genomic and transcriptomic data of N. gaditana B-31 reported above has PubMed ID: 23966634 and is available at the url: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23966634
Happy browsing at the NCBI 
We added a new feature to the Bibliography: “Altmetric donuts” close to each publication listed in the page.
What are the Article Level metrics (Altmetric) ?

Altmetrics give a measure of the digital impact and reach of an article by combining a selection of online indicators (both scholarly and non-scholarly) . They do this by tracking, collecting and measuring large amounts of data collected from all of the places where people talk about science online – for example, blogs, Twitter, Facebook, Google+, message boards and mainstream newspapers and magazines. Altmetric allows authors and publishers to see what people are saying about a scholarly paper and can tell them how much attention a paper is receiving relative to their peers.
The Altmetric donuts are a representation of the Altmetric information:
- the number in the centre of the donut is the Altmetric score (e.g. the absolute number of citations in the media);
- the colours surrounding the donut reflect the mix of sources mentioning that score – blue for Twitter, yellow for blogs, red for mainstream media sources and so on;
- by clicking on the donut you access a page with the details of the Altmetric analysis
The score is automatically updated every week, so that the followers of the blog can access real time information about the attention that is developing around each of the listed papers.
We encourage you to submit your paper to the blog to increase the reach of your achievements!
]]>![]() We updated our FTP area, now including datasets from other Nannochloropsis species and strains and the list of families of orthologous proteins obtained from the comparison of N. gaditana and N. oceeanica predicted proteins.
We updated our FTP area, now including datasets from other Nannochloropsis species and strains and the list of families of orthologous proteins obtained from the comparison of N. gaditana and N. oceeanica predicted proteins.
 Are you an expert about Nannochloropsis? Is your research focused on this organism?
Are you an expert about Nannochloropsis? Is your research focused on this organism?
Consider becoming a new author of this blog and contributing to the scientific discussion!
Why don’t you start with advertising your recent publication or commenting on the posts of this blog?
Is there any hot topic that you would like to discuss or any suggestion that you would like to ask to this scientific community?
Fill this form and we will be happy to consider you application as new author
[contact-form to=’[email protected]%26#x002c; [email protected]’ subject=’application for becoming a new author of Nannochloropsis blog’][contact-field label=’Name’ type=’name’ required=’1’/][contact-field label=’Email’ type=’email’ required=’1’/][contact-field label=’Position / Title ‘ type=’url’/][contact-field label=’Expertise or Research line’ type=’textarea’ required=’1’/][/contact-form]
follow us on researchgate!
]]>We currently have more than 1.000 unique visitors per month, accounting for roughly 18,000 pageviews per month. Visitors are spread across the four continents… Thank you for keeping alive Nannochloropsis.org. We are doing our best to update this site and we are also preparing new resources (to be released soon).

This week’s visits
]]>
Upon user request we uploaded the GFF version of Nannochloropsis gaditana annotation. This file is in standard GFF3 format, and features refers to the assembled genome (i.e. scaffolds).
You can download the file from the Nannochloropsis genome FTP area.
]]>Our paper “Chromosome scale genome assembly and transcriptome profiling of Nannochloropsis gaditana in nitrogen depletion” is online.
You can access it from the Publisher’s website.
Now available an on line form to share your findings with the Nanncohloropsis scientific community!
By completing the on line form you will advertise your paper through our Bibliography page and you will signal to the “nannochloropsis.org” personell how to update the databases integrating your new findings!
We will integrate your data as soon as possibile. And we will be pleased to open a discussion on your new findings in this blog with your help!
]]>